 |
Morse Micro IoT SDK
2.9.7
|
 |
Morse Micro IoT SDK
2.9.7
|
Emmet is a firmware subsystem that allows various aspects of the firmware to be driven by a connected computer.
This is intended as an aid for development and automated test.
Examples of functionality that can be driven by Emmet include:
A high-level block diagram of how Emmet fits into the overall firmware architecture is shown below. Emmet provides an API to an connected computer, interfaced via the debug interface of the MCU, that is able invoke functions at various layers of the firmware stack.
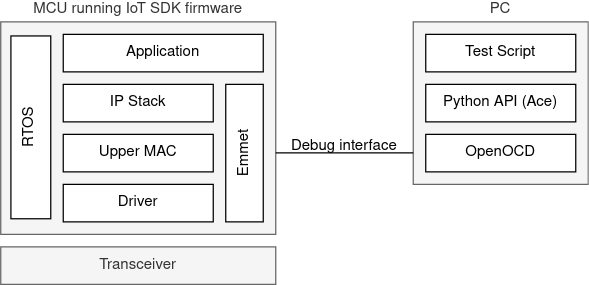
The Emmet Control API (Ace) is a Python library that abstracts away the details of the protocol used by the PC to communicate with the Emmet subsystem via OpenOCD, and provides an easy-to-use interface to the Emmet API. This enables control scripts to be written in Python, examples of which are provided as part of this SDK.
There are two aspects to enabling Emmet support in an application. Firstly, the application must invoke emmet_init() to initialize Emmet, and emmet_start() to start Emmet.
Secondly, the .emmet_hostif_table section must be located at address 0x20000400. (Note that a different address may be used if it is not possible to locate .emmet_hostif_table at this address then, but it will be necessary to update the Python API.)
The following code can be added to the platform linker script to place the .emmet_hostif_table section at the correct location:
Note that the linker script provided with the SDK includes the above code snippet so that the Emmet section is located at the correct address.
A number of Python scripts are provided in the tools/ace/examples directory. These can be used to perform various operations from the command line. See How to use the Emmet example application for more.
Functions | |
| void | emmet_init (void) |
| Initialize Emmet. More... | |
| void | emmet_start (void) |
| Start Emmet. More... | |
| enum mmwlan_status | emmet_set_reg_db (const struct mmwlan_regulatory_db *reg_db) |
| Set the regulatory database for Emmet to use. More... | |
| void emmet_init | ( | void | ) |
Initialize Emmet.
This will zero the host interface table but will not set the magic number, so it will not accept commands from the host until emmet_start() is invoked.
| enum mmwlan_status emmet_set_reg_db | ( | const struct mmwlan_regulatory_db * | reg_db | ) |
Set the regulatory database for Emmet to use.
| reg_db | The regulatory database to use. Must remain valid in memory. |
MMWLAN_SUCCESS on success, or another relevant error code. | void emmet_start | ( | void | ) |
Start Emmet.
This will set the magic number in the host interface table so that the host knows it can now begin sending commands to Emmet.